Table of Contents:
Introduction
In the ever-evolving field of healthcare, the need for accurate and timely information is crucial. Knowledge management systems used in healthcare play a vital role in ensuring that healthcare professionals have access to the right information at the right time. These systems help in organizing, storing, and retrieving critical medical data, which can significantly improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare operations. This article explores how knowledge management systems can enhance various aspects of healthcare practices, from clinical decision-making to compliance with regulations.
What Are Knowledge Management Systems?
Knowledge management systems (KMS) are tools and processes designed to capture, store, manage, and share knowledge within an organization. In the context of healthcare, these systems help in managing vast amounts of medical data, clinical guidelines, patient records, and research findings. The primary goal of a KMS is to ensure that valuable information is easily accessible to healthcare professionals when they need it most.
Key components of a knowledge management system include:
- Data Repositories: Centralized databases where information is stored and organized.
- Search and Retrieval Tools: Features that allow users to quickly find the information they need.
- Collaboration Platforms: Tools that enable healthcare teams to share knowledge and work together effectively.
- Analytics and Reporting: Capabilities that help in analyzing data and generating insights for better decision-making.
By integrating these components, knowledge management systems can transform raw data into actionable insights, ultimately enhancing the quality of care provided to patients.
The chart illustrates the adoption rate of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) in hospitals from 2010 to 2020. Here are the specific numbers:
Percentage of Hospitals Using EHRs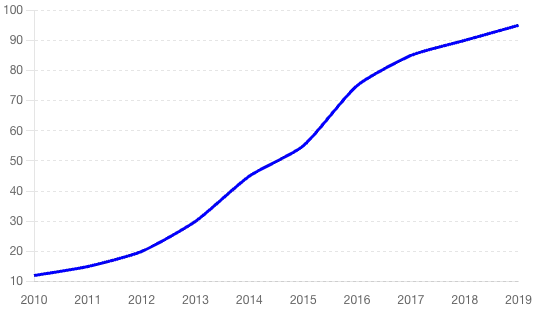
Benefits and Challenges of Knowledge Management Systems in Healthcare
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Decision-Making | Access to up-to-date research, comprehensive patient data, decision support tools. | Initial cost, resistance to change, data privacy concerns. |
| Patient Care Coordination | Unified patient records, real-time updates, task management, communication tools. | Integration challenges, implementation complexity. |
| Telemedicine | Remote access to information, patient self-service portals, secure communication. | Technology barriers, data security issues. |
| Clinical Research | Centralized data repositories, collaboration tools, advanced analytics. | Data integrity concerns, regulatory compliance hurdles. |
| Professional Development | Access to educational materials, online training programs, knowledge sharing. | Ongoing maintenance cost, need for continuous updates. |
| Process Efficiency | Standardized protocols, automated workflows, efficient information retrieval. | Customization needs, initial setup complexity. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Secure data management, thorough documentation, policy and procedure management. | Compliance with evolving regulations. |
Importance of Knowledge Management Systems in Healthcare
The importance of knowledge management systems in healthcare cannot be overstated. These systems play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery. By providing healthcare professionals with easy access to up-to-date information, KMS help in making informed decisions, improving patient care, and reducing errors.
Here are some key reasons why knowledge management systems are essential in healthcare:
- Improved Clinical Decision-Making: Access to the latest research, clinical guidelines, and patient data helps doctors and nurses make better decisions.
- Enhanced Patient Care Coordination: KMS facilitate seamless communication and information sharing among healthcare teams, ensuring that all team members are on the same page.
- Support for Telemedicine: With the rise of telemedicine, having a robust KMS ensures that remote consultations are as effective as in-person visits.
- Advancement in Clinical Research: Researchers can easily access and share data, accelerating the pace of medical discoveries and innovations.
- Professional Development: Continuous learning is vital in healthcare. KMS provide resources for ongoing education and training.
- Streamlined Processes: Efficient management of information leads to smoother operations and reduced administrative burdens.
- Regulatory Compliance: KMS help healthcare organizations comply with regulations such as HIPAA by ensuring that data is managed securely and responsibly.
In summary, knowledge management systems are indispensable tools that support various aspects of healthcare, from clinical practice to research and administration.
Enhancing Clinical Decision-Making
One of the most significant benefits of knowledge management systems used in healthcare is their ability to enhance clinical decision-making. Accurate and timely decisions are critical in healthcare, where the stakes are often life and death. KMS provide healthcare professionals with access to a wealth of information, enabling them to make well-informed decisions quickly.
Here are some ways in which KMS enhance clinical decision-making:
- Access to Up-to-Date Research: Healthcare professionals can access the latest research findings and clinical guidelines, ensuring that their decisions are based on the most current evidence.
- Comprehensive Patient Data: KMS integrate patient records, lab results, and medical histories, providing a holistic view of the patient's health status.
- Decision Support Tools: Many KMS include decision support tools that offer recommendations based on best practices and clinical protocols.
- Reducing Diagnostic Errors: By providing comprehensive information, KMS help reduce the likelihood of diagnostic errors, leading to more accurate diagnoses and better patient outcomes.
- Collaboration and Consultation: KMS facilitate collaboration among healthcare teams, allowing for multiple perspectives and expertise to be considered in decision-making.
For example, a doctor treating a patient with a rare condition can use a KMS to quickly access relevant case studies, research articles, and treatment protocols. This access to information helps the doctor make a more informed decision about the best course of action for the patient.
In summary, knowledge management systems are invaluable tools that support healthcare professionals in making better, faster, and more accurate clinical decisions.
Coordinating Patient Care
Effective patient care coordination is essential for delivering high-quality healthcare services. Knowledge management systems used in healthcare play a pivotal role in ensuring that all members of a healthcare team have access to the same information, thereby improving coordination and collaboration.
Here are some ways in which KMS facilitate better patient care coordination:
- Unified Patient Records: KMS consolidate patient information from various sources into a single, comprehensive record. This ensures that all healthcare providers have access to the same data, reducing the risk of errors and omissions.
- Real-Time Updates: When a patient's condition changes or new information becomes available, KMS can provide real-time updates to all relevant healthcare providers. This ensures that everyone is working with the most current information.
- Task Management: KMS often include tools for assigning and tracking tasks, ensuring that all aspects of patient care are managed efficiently. This helps in avoiding duplication of efforts and ensures that nothing is overlooked.
- Communication Tools: Many KMS include built-in communication tools, such as secure messaging and video conferencing, which facilitate seamless communication among healthcare team members.
- Care Pathways: KMS can help in defining and managing care pathways, ensuring that patients receive consistent and coordinated care across different stages of their treatment.
For instance, a patient undergoing surgery may require coordinated care from surgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, and physical therapists. A KMS ensures that all these professionals have access to the same patient information and can communicate effectively, leading to better coordinated and more efficient care.
In conclusion, knowledge management systems are crucial for improving patient care coordination, ensuring that healthcare teams work together seamlessly to provide the best possible care.
Supporting Telemedicine and Self-Service Operations
The rise of telemedicine and self-service operations has transformed the healthcare landscape. Knowledge management systems used in healthcare are instrumental in supporting these modern healthcare delivery methods. By providing a robust infrastructure for information sharing and management, KMS ensure that remote healthcare services are effective and reliable.
Here are some ways in which KMS support telemedicine and self-service operations:
- Remote Access to Information: KMS allow healthcare providers to access patient records, clinical guidelines, and other essential information from any location. This is crucial for telemedicine, where providers may be consulting with patients from different geographical areas.
- Patient Self-Service Portals: Many KMS include features that enable patients to access their own medical records, schedule appointments, and communicate with healthcare providers. This empowers patients to take an active role in managing their health.
- Secure Communication: KMS provide secure platforms for communication between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring that sensitive information is protected. This is particularly important for telemedicine consultations.
- Integration with Telehealth Tools: KMS can integrate with various telehealth tools, such as video conferencing software and remote monitoring devices, to provide a seamless experience for both patients and providers.
- Educational Resources: KMS can offer a wealth of educational materials for patients, helping them understand their conditions and treatment options. This is especially useful for self-service operations, where patients may need to make informed decisions about their care.
For example, a patient with a chronic condition can use a self-service portal to monitor their health metrics, access educational resources, and communicate with their healthcare provider. The provider, in turn, can use the KMS to review the patient's data and offer personalized advice during a telemedicine consultation.
In summary, knowledge management systems are essential for supporting telemedicine and self-service operations, ensuring that both patients and healthcare providers have the information and tools they need for effective remote care.
Advancing Clinical Research and Development
Clinical research and development (R&D) are fundamental to advancing medical science and improving patient care. Knowledge management systems used in healthcare play a critical role in facilitating these activities by providing a structured way to manage and share research data and findings.
Here are some ways in which KMS advance clinical research and development:
- Centralized Data Repositories: KMS provide centralized repositories where researchers can store and access vast amounts of data, including clinical trial results, patient outcomes, and research publications. This centralization makes it easier to find and use relevant information.
- Collaboration Tools: KMS include tools that facilitate collaboration among researchers, allowing them to share data, insights, and findings in real-time. This enhances teamwork and accelerates the research process.
- Data Analytics: Advanced analytics capabilities within KMS help researchers analyze large datasets to identify trends, correlations, and insights that can inform future studies and clinical practices.
- Compliance and Security: KMS ensure that research data is managed in compliance with regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA, and that sensitive information is protected through robust security measures.
- Knowledge Sharing: KMS facilitate the dissemination of research findings through publications, presentations, and other channels, ensuring that valuable knowledge is shared with the broader medical community.
For example, a research team studying a new treatment for diabetes can use a KMS to store and analyze patient data from clinical trials. The system can help them identify patterns and outcomes, collaborate with other researchers, and share their findings with the medical community. This streamlined process accelerates the pace of discovery and ensures that new treatments reach patients more quickly.
In conclusion, knowledge management systems are indispensable for advancing clinical research and development, providing the tools and infrastructure needed to manage data, collaborate effectively, and share valuable insights.
Facilitating Professional Development
Continuous professional development is crucial in the healthcare sector, where medical knowledge and technologies are constantly evolving. Knowledge management systems used in healthcare provide valuable resources and tools that support the ongoing education and training of healthcare professionals.
Here are some ways in which KMS facilitate professional development:
- Access to Educational Materials: KMS offer a repository of educational resources, including research articles, clinical guidelines, training modules, and e-learning courses. These materials help healthcare professionals stay updated with the latest advancements in their field.
- Online Training Programs: Many KMS include platforms for online training and certification programs. These programs allow healthcare professionals to acquire new skills and knowledge at their own pace and convenience.
- Knowledge Sharing and Collaboration: KMS facilitate the sharing of knowledge and best practices among healthcare professionals. Forums, discussion boards, and collaborative tools enable practitioners to learn from each other’s experiences and expertise.
- Performance Tracking: KMS can track the progress and performance of healthcare professionals in their training programs. This helps in identifying areas where additional training may be needed and ensures that staff meet the required competencies.
- Continuing Medical Education (CME): KMS support CME by providing access to accredited courses and materials that healthcare professionals need to maintain their licensure and certifications.
For instance, a nurse looking to specialize in pediatric care can use a KMS to access specialized training modules, participate in online courses, and collaborate with experienced pediatric nurses. This comprehensive approach to professional development ensures that the nurse is well-prepared to provide high-quality care to young patients.
In summary, knowledge management systems are essential for facilitating professional development in healthcare, providing the resources and tools needed for continuous learning and skill enhancement.
Streamlining Processes and Procedures
Streamlining processes and procedures is vital for improving efficiency and reducing costs in healthcare. Knowledge management systems used in healthcare play a crucial role in optimizing these processes by providing a structured approach to managing information and workflows.
Here are some ways in which KMS streamline processes and procedures:
- Standardized Protocols: KMS help in creating and disseminating standardized protocols and guidelines. This ensures that all healthcare providers follow best practices, reducing variability and improving consistency in patient care.
- Automated Workflows: Many KMS include features for automating routine tasks and workflows. This reduces the administrative burden on healthcare staff and allows them to focus more on patient care.
- Efficient Information Retrieval: KMS provide quick and easy access to information, reducing the time spent searching for data. This speeds up decision-making and enhances productivity.
- Performance Monitoring: KMS include tools for monitoring and analyzing performance metrics. This helps in identifying bottlenecks and areas for improvement, leading to more efficient operations.
- Resource Management: KMS assist in managing resources such as medical supplies, equipment, and staff schedules. This ensures optimal utilization of resources and reduces waste.
For example, a hospital can use a KMS to implement standardized treatment protocols for common conditions like hypertension. The system can automate the workflow for patient intake, diagnosis, and treatment, ensuring that all steps are followed correctly and efficiently. Additionally, performance metrics can be monitored to identify any deviations from the protocol and make necessary adjustments.
In conclusion, knowledge management systems are essential for streamlining processes and procedures in healthcare, leading to more efficient operations and better patient outcomes.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with regulations is a critical aspect of healthcare operations. Knowledge management systems used in healthcare play a vital role in ensuring that healthcare organizations adhere to various regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA in the United States.
Here are some ways in which KMS help ensure compliance with regulations:
- Secure Data Management: KMS provide robust security measures to protect sensitive patient information. This includes encryption, access controls, and audit trails, ensuring that data is handled in compliance with privacy regulations.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: KMS facilitate accurate and thorough documentation of patient care and administrative processes. This helps in maintaining records that are required for regulatory compliance and audits.
- Policy and Procedure Management: KMS allow healthcare organizations to create, update, and disseminate policies and procedures that comply with regulatory standards. This ensures that all staff members are aware of and follow the required guidelines.
- Training and Education: KMS provide resources for training healthcare professionals on regulatory requirements and best practices. This ensures that staff are knowledgeable about compliance issues and know how to adhere to them.
- Monitoring and Reporting: KMS include tools for monitoring compliance with regulations and generating reports. This helps in identifying any areas of non-compliance and taking corrective actions promptly.
For example, a healthcare organization can use a KMS to manage and document compliance with HIPAA regulations. The system can ensure that all patient data is encrypted and access is restricted to authorized personnel. Additionally, the KMS can provide training modules on HIPAA compliance for staff and generate audit reports to demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements.
In summary, knowledge management systems are essential for ensuring compliance with regulations in healthcare, providing the tools and infrastructure needed to manage data securely, document processes accurately, and train staff effectively.
Steps for Implementing Knowledge Management Systems
Implementing knowledge management systems used in healthcare requires careful planning and execution. Here are the key steps to ensure a successful implementation:
- Engage the Entire Team: Involve all stakeholders, including healthcare providers, administrative staff, and IT professionals, from the beginning. Their input and buy-in are crucial for the system's success.
- Define the Value Proposition: Clearly articulate the benefits of the knowledge management system. Explain how it will improve patient care, streamline operations, and support compliance with regulations.
- Identify Stakeholders and Roles: Assign specific roles and responsibilities to team members. Identify key stakeholders, such as project managers, data stewards, and compliance officers, who will oversee different aspects of the implementation.
- Conduct a Needs Assessment: Evaluate the current state of knowledge management within the organization. Identify gaps and areas for improvement to tailor the system to meet specific needs.
- Select the Right KMS: Choose a knowledge management system that aligns with the organization's goals and requirements. Consider factors such as scalability, ease of use, integration capabilities, and security features.
- Develop a Implementation Plan: Create a detailed plan that outlines the steps, timeline, and resources needed for the implementation. Include milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress.
- Provide Training and Support: Ensure that all users receive comprehensive training on how to use the KMS effectively. Offer ongoing support to address any issues and encourage adoption.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor the system's performance and gather feedback from users. Evaluate the impact of the KMS on healthcare practices and make necessary adjustments to optimize its effectiveness.
For example, Dr. Cynthia J. Young from CJ Young Consulting emphasizes the importance of communities of practice (CoP) and knowledge mapping during the onboarding process. These strategies help in identifying key knowledge areas and ensuring that the right information is accessible to the right people.
In summary, implementing a knowledge management system in healthcare involves engaging the entire team, defining the value proposition, assigning roles, conducting a needs assessment, selecting the right system, developing a detailed plan, providing training, and continuously monitoring and evaluating the system's performance.
Case Study: WHO's TRACK Initiative
The World Health Organization's (WHO) TRACK Initiative is a prime example of how knowledge management systems used in healthcare can make a significant impact. Launched in 2023, the TRACK Initiative aims to address advanced HIV disease (AHD), which resulted in approximately 650,000 deaths in 2021.
Here are some key aspects of the TRACK Initiative and how knowledge management systems play a role:
- Data Collection and Analysis: The initiative relies on KMS to collect and analyze data from various sources, including patient records, clinical trials, and field reports. This data-driven approach helps in identifying trends and tailoring interventions to specific needs.
- Knowledge Sharing: KMS facilitate the sharing of best practices, research findings, and treatment protocols among healthcare providers involved in the initiative. This ensures that all stakeholders have access to the latest information and can implement evidence-based practices.
- Training and Capacity Building: The TRACK Initiative uses KMS to provide training and educational resources to healthcare workers. This helps in building the capacity of local healthcare systems to manage and treat AHD effectively.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: KMS enable continuous monitoring and evaluation of the initiative's impact. This includes tracking patient outcomes, assessing the effectiveness of interventions, and making data-driven adjustments to improve results.
- Collaboration and Coordination: The initiative involves multiple stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and healthcare providers. KMS support collaboration and coordination among these stakeholders, ensuring a unified and effective response to AHD.
For example, healthcare providers in different regions can use the KMS to access standardized treatment protocols for AHD, share patient data securely, and participate in virtual training sessions. This collaborative approach enhances the overall effectiveness of the initiative and improves patient outcomes.
In conclusion, the WHO's TRACK Initiative demonstrates the power of knowledge management systems in addressing complex healthcare challenges. By leveraging data, facilitating knowledge sharing, and supporting collaboration, KMS play a crucial role in the success of such initiatives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knowledge management systems used in healthcare are indispensable tools that enhance various aspects of healthcare delivery. From improving clinical decision-making and coordinating patient care to supporting telemedicine and advancing clinical research, KMS provide a robust framework for managing and sharing critical information.
By streamlining processes, ensuring compliance with regulations, and facilitating professional development, KMS contribute to more efficient and effective healthcare operations. The successful implementation of these systems requires careful planning, engagement of the entire team, and continuous monitoring and evaluation.
As demonstrated by initiatives like WHO's TRACK, the impact of KMS in healthcare can be profound, leading to better patient outcomes and more informed healthcare practices. Embracing knowledge management systems is not just a technological upgrade; it is a strategic move towards a more connected, informed, and efficient healthcare system.
Experiences and Opinions
Healthcare professionals report significant improvements after implementing knowledge management systems. Many users find that these systems streamline access to crucial information. For instance, a hospital introduced a centralized database. Staff can now quickly retrieve patient histories and treatment protocols. This change reduced the time spent searching for information by over 30%.
Another common experience involves better communication among teams. Healthcare workers emphasize that knowledge management systems facilitate real-time updates. This feature is especially useful during emergencies. Hospitals using these systems report fewer errors in patient care. Misdiagnoses and medication errors decrease significantly when staff can access accurate data instantly.
However, challenges remain. Some users mention difficulties in integrating new systems with existing workflows. A report highlights that many healthcare providers struggle with outdated technology. This can lead to frustration among staff who are accustomed to manual processes. Users express that without proper training, the transition can be overwhelming.
On the positive side, many professionals appreciate automated alerts for critical updates. This feature allows for proactive patient care. For example, alerts can notify staff about abnormal lab results. Quick responses can lead to better patient outcomes, as timely interventions are crucial in healthcare.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Collaboration improves significantly with these systems. Users often comment on how easy it becomes to share knowledge across departments. A nurse shared that her team now conducts regular meetings using data from the knowledge management system. This sharing of information enhances teamwork and reduces silos.
Moreover, onboarding processes benefit greatly. New employees find it easier to acclimate when they have access to comprehensive resources. Feedback indicates that well-structured knowledge repositories improve retention rates. Users report feeling more confident in their roles, knowing that the information they need is readily accessible.
Impact on Patient Safety
Patient safety is a top concern for healthcare providers. Many users highlight that effective knowledge management reduces risks. For instance, a healthcare facility noted a significant drop in medication errors after implementing a knowledge management system. Staff reported being able to double-check dosages through the system before administration.
Despite these advantages, some users raise concerns about data security. They worry that centralized systems may become targets for cyberattacks. A healthcare provider mentioned the importance of robust security measures to protect sensitive patient information. Ensuring compliance with regulations is critical to maintaining trust.
In summary, knowledge management systems play a crucial role in enhancing healthcare practices. Users experience improved communication, collaboration, and patient safety. Despite some integration challenges and security concerns, the overall feedback is positive. The right system can transform healthcare operations significantly.
For further insights, see this review on knowledge management software and these proven strategies for effective knowledge management in healthcare.
FAQ on Knowledge Management Systems in Healthcare
What are Knowledge Management Systems (KMS) in healthcare?
Knowledge Management Systems (KMS) in healthcare are tools and processes designed to capture, store, manage, and share knowledge within a healthcare organization. They help in managing medical data, clinical guidelines, patient records, and research findings to ensure valuable information is easily accessible to healthcare professionals when needed.
How do KMS improve clinical decision-making?
KMS improve clinical decision-making by providing access to up-to-date research, clinical guidelines, and comprehensive patient data. Decision support tools and reduced diagnostic errors also contribute to more accurate and efficient clinical decisions.
What are the benefits of KMS in coordinating patient care?
KMS facilitate better patient care coordination by consolidating patient information into unified records, providing real-time updates, aiding in task management, and offering communication tools. This ensures seamless communication and information sharing among healthcare teams.
How do KMS support telemedicine and self-service operations?
KMS support telemedicine and self-service operations by allowing remote access to information, providing patient self-service portals, ensuring secure communication, integrating with telehealth tools, and offering educational resources for patients.
Why are KMS important for ensuring regulatory compliance in healthcare?
KMS are crucial for ensuring regulatory compliance by providing secure data management, thorough documentation and record-keeping, managing policies and procedures, offering training on regulatory requirements, and monitoring compliance through reporting tools.





